
8032334610

Medicare Advantage – Part C
You must enroll in Original Medicare before enrolling into Medicare Advantage.
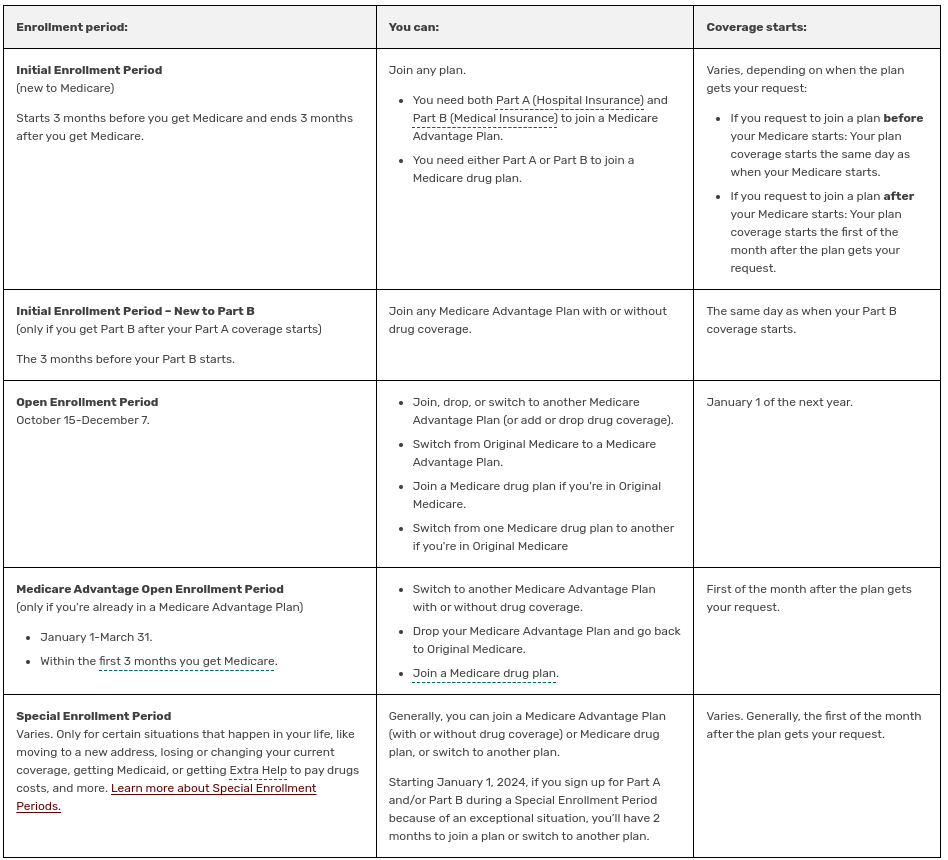
Initial Enrollment Period (IEP)
The IEP is a 7-month period that begins 3 months before the month you turn sixty-five and ends 3 months after you turn sixty-five. For someone under age 65 who becomes entitled to Medicare based on disability, entitlement begins with the 25th month of disability benefit entitlement. For these individuals, the IEP begins 3 months before the 25th month of disability benefit entitlement, includes the 25th month, and ends three months after. The IEP for people with ESRD and ALS varies based on their situation.
Coverage begins based on when you enroll. If you enroll in the first 3 months of the IEP, coverage begins the month you are eligible for Medicare. Disabled individuals enroll automatically into Medicare Part A and Part B after 24 months of receiving Social Security disability benefits.
NOTE: In most cases, if someone does not enroll in Part B when first eligible, they will have to pay a late enrollment penalty when they enroll.
General Enrollment Period (GEP)
The GEP takes place from January 1 through March 31 of each year. Part B and Part A coverage begins July 1 of that same year.
Special Enrollment Period (SEP) for the Working Aged and Working Disabled.
Individuals who do not enroll in Part B when first eligible because they were insured under a group health plan based on their own or a spouse's current employment (or the current employment of a family member, if disabled) may enroll during the SEP. The individual can enroll at any time while covered under the group health plan based on current employment, or during the 8-month period that begins the month the employment ends or the group health plan coverage ends, whichever comes first.
So, what is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage plans offered by Private Insurance companies. Also known as Part C, Medicare Advantage combines HOSPITAL (PART A) and MEDICAL (PART B) into ONE plan.
Most Medicare Advantage plans include prescription drug coverage Part D and may offer additional benefits not provided by Original Medicare.
Several kinds of Medicare Advantage plans are offered by Private Insurance companies. The name of plan will usually indicate the type of benefit structure which can help you choose the plan that works best for your situation. The following
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) - specific provider network
HMO Point-of-Service (HMO-POS) - HMO network plus additional providers who agree to accept the terms specified by in insurance company.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) - specifies in-network plus out-of-network providers. Costs to insured various based upon the provider's contract.
Private Fee-for-Service (PFFS) - can offer full or partial networks of providers, or, in certain cases, they may not use a network of providers at all.
Special Needs Plan (SNP) - coordinated care plan (CCP) specifically designed to provide targeted care and limit enrollment to special needs individuals.
Dual Special Needs Plan (D-SNP) Medicare/Medicaid - (Dual-eligible) offered to Medicare Beneficiaries who are also qualified and enrolled in Medicaid.
Medicare Medical Savings Account (MSA) - combines a high-deductible health plan with a medical savings account.
Why Choose Medicare Advantage Plan Enrollment?
If you enrolled in Original Medicare, then you are also eligible for the Medicare Advantage plan (also known as Part C). Original Medicare includes Part A (hospital costs) and Part B (medical costs). However, Original Medicare does not cover prescription drugs or hearing, vision, or dental care.
Unlike Original Medicare, which has the government pay for your Medicare benefits, Medicare Advantage has private companies pay for your Medicare benefits. When you choose a Medicare Advantage plan, you can have more options and coverage for your health care.
Depending on the company providing the insurance, Medicare Advantage gives you hearing, vision, and dental care, along with prescription drug coverage. Plans can offer you coverage outside of the U.S., while Original Medicare does not. Medicare Advantage can also be less expensive than Original Medicare.